| Section | Summary |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Overview of noise-cancelling technology and its importance in modern headphones. |
| Active vs Passive Noise-Cancelling | Distinguishes between two main types: passive (isolation) and active (ANC). |
| How Active Noise-Cancelling Works | Detailed explanation of active noise cancellation using microphones, anti-noise, and processing. |
| Types of Active Noise-Cancelling | Highlights various ANC approaches, including feedforward and feedback systems. |
| Challenges and Limitations | Explains where ANC technology can struggle, such as high-frequency or sudden sounds. |
| Applications of ANC | Lists practical uses for ANC headphones, from travel to office work. |
| Conclusion | Recap of ANC’s benefits and outlook for future development. |
Introduction
Noise-cancelling technology has revolutionized the headphone industry by significantly reducing ambient sounds, allowing users to focus on their audio content. Whether you’re on a noisy airplane or working in a bustling café, noise-cancelling headphones can make all the difference.
The key to their functionality lies in a technology known as active noise cancellation (ANC), which actively counters external noise using microphones and sophisticated audio processing.
Active vs Passive Noise-Cancelling

Before diving into the workings of active noise-cancelling technology, it’s essential to understand the two primary forms of noise cancellation:
- Passive Noise-Cancelling (Noise Isolation): This method relies on the physical design of the headphones, which block sound through tightly sealed ear cups. While effective at muffling higher frequencies, this type of cancellation doesn’t perform well for lower-frequency noises like engine hums or air conditioning drones.
- Active Noise-Cancelling (ANC): This is a more advanced technology that actively reduces unwanted sound through a process called “destructive interference.”
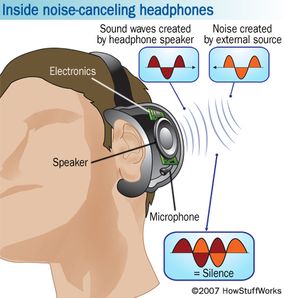
How Active Noise-Cancelling Works
The heart of noise-cancelling technology lies in active noise control (ANC), which is made possible through several components that work together seamlessly:
- Microphones: Noise-cancelling headphones have built-in microphones that detect external sounds. These microphones are often placed both inside and outside the ear cups to capture a wide range of ambient noise.
- Anti-noise Signal: Once the microphone detects external sounds, a signal processor generates an “anti-noise” wave. This anti-noise signal has the same amplitude but an opposite phase to the unwanted sound wave, effectively canceling it out through a phenomenon called destructive interference.
- Real-time Processing: The noise-cancelling process happens in real-time. The digital signal processor (DSP) inside the headphones constantly analyzes incoming noise and creates the corresponding anti-noise wave to cancel it.
This continuous feedback loop ensures that low-frequency, constant noise, such as the hum of an airplane engine, is dramatically reduced, allowing for a more peaceful listening experience.
Types of Active Noise-Cancelling
Not all ANC systems are created equal. Depending on the type of ANC headphones, manufacturers might use different configurations to optimize sound cancellation. Here are the most common types:
- Feedforward ANC: In this system, microphones are placed on the outside of the headphones to detect and cancel noise before it enters the ear. While simple, feedforward ANC can sometimes struggle with unexpected or high-frequency sounds because the microphones don’t detect the noise inside the ear cup.
- Feedback ANC: Feedback systems use microphones inside the ear cups. These microphones pick up noise that has already entered the ear, providing an accurate representation of what the user hears and canceling that noise more effectively.
- Hybrid ANC: A combination of feedforward and feedback ANC, hybrid systems utilize microphones both inside and outside the ear cups. This configuration offers better noise cancellation across a wider range of frequencies, making it the most advanced form of ANC.
Challenges and Limitations of Noise-Cancelling Technology
Despite its benefits, noise-cancelling technology isn’t perfect and comes with a few challenges:
- High-frequency sounds such as sudden car honks or loud voices are more difficult to cancel out. ANC is more effective at reducing low-frequency sounds like engines or air conditioning hums.
- Battery dependence: ANC headphones rely on active electronic components, meaning they require a power source, typically rechargeable batteries. The active noise-cancelling feature may stop functioning once the battery is drained, leaving users with standard passive noise isolation.
- Pressure on the ears: Some users experience discomfort or a feeling of pressure on their ears due to the constant processing and the anti-noise waves produced by the headphones.
Applications of Noise-Cancelling Technology
Noise-cancelling headphones are incredibly versatile and beneficial in various environments:
- Travel: ANC headphones are a staple for frequent flyers, helping to reduce the constant drone of airplane engines and make long trips more comfortable.
- Work: In open-office settings or crowded cafés, ANC can help you focus by blocking out background conversations and office equipment noise.
- Relaxation: Whether you’re meditating or just trying to enjoy some peace and quiet, noise-cancelling headphones can create an isolated space for calm.
Conclusion
Noise-cancelling technology has significantly enhanced the headphone experience, allowing users to enjoy their audio without the constant intrusion of external sounds. With ongoing improvements in active noise control (ANC), these headphones are becoming more efficient, comfortable, and accessible for everyday use.
As the technology evolves, we can expect even better noise-cancellation performance, making it a must-have feature in modern headphones.
References
Active Noise Control on Wikipedia
How Noise-Cancelling Technology Works
Bang & Olufsen on ANC